Role of Synbiotic additive on Chicken Gut Microflora for Disease Control and Production Efficiency: A Narrative Review
Keywords:
Chicken, Immunity, Infectious Disease, Feed additive, Gut Microbiota, Health, poultry, SynbioticAbstract
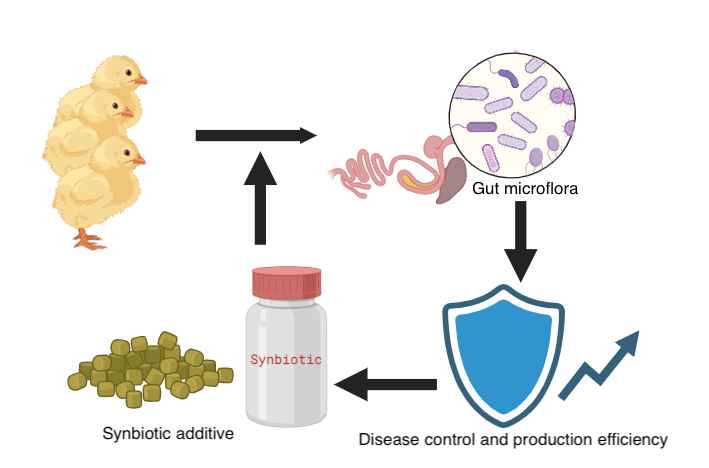
The use of synbiotic additives in chicken feed improves gut microbiota and represents a promising approach to bolster protective immunity against infectious diseases and enhance production efficiency. These additives, which encompass probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics, are essential in modulating the microbiota of the chicken, thus promoting gut health. This narrative review aimed to explore the application of synbiotic feed additives to enhance gut microflora and mucosal immunity to disease control and improve production efficiency in chickens. In poultry production, infectious diseases are among the major challenges. Chickens may acquire these diseases either from external sources or from opportunistic pathogens that normally exist within their bodies. Most commensal bacteria reside in the gastrointestinal tract, where they form the gut microbiota. This microbiota, which begins to establish immediately after hatching, is essential for the health and well-being of chickens. The gut microbiota includes both beneficial and opportunistic pathogens. While medications are used to control infections and promote growth, excessive antibiotic use in poultry disrupts this balance, leading to negative health effects. To promote a balanced intestinal microbiota in chickens, beneficial microbes can be provided through synbiotic feed additives. This strategy can improve gut health for better nutrient absorption, strengthen mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue to enhance immunity, and potentially reduce reliance on antibiotics. Synbiotics generally have beneficial effects on host biological functions, acting as immunomodulators and promoting growth in chickens. They help limit pathogen colonization and enhance overall performance. Therefore, poultry producers should be encouraged to incorporate synbiotic-based feed supplements.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Asnakew Mulaw Berihun (Corresponding Author); Zenebe Jemere, Bemrew Admassu, Dejen Takele, Yitayew Demessie (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.