Role of Synbiotic additive on Chicken Gut Microflora for Disease Control and Production Efficiency: A Narrative Review
Keywords:
Chicken, Immunity, Infectious Disease, Feed additive, Gut Microbiota, Health, poultry, SynbioticAbstract
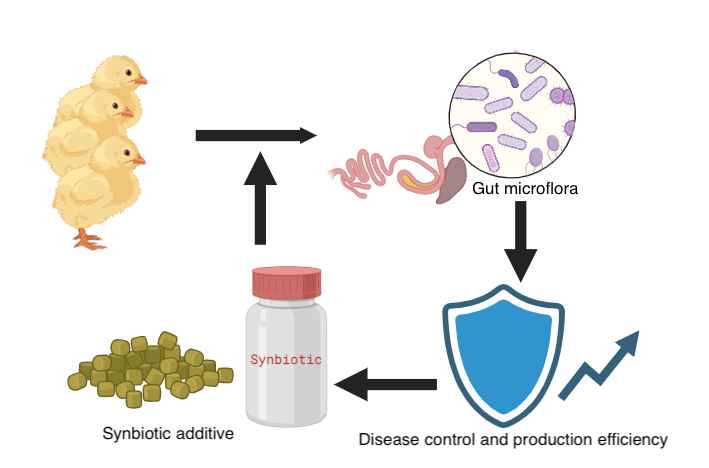
The use of synbiotic additives in chicken feed improves gut microbiota and represents a promising approach to bolster protective immunity against infectious diseases and enhance production efficiency. These additives, which encompass probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics, are essential in modulating the microbiota of the chicken, thus promoting gut health. This narrative review aimed to explore the application of synbiotic feed additives to enhance gut microflora and mucosal immunity to disease control and improve production efficiency in chickens. In poultry production, infectious diseases are among the major challenges. Chickens may acquire these diseases either from external sources or from opportunistic pathogens that normally exist within their bodies. Most commensal bacteria reside in the gastrointestinal tract, where they form the gut microbiota. This microbiota, which begins to establish immediately after hatching, is essential for the health and well-being of chickens. The gut microbiota includes both beneficial and opportunistic pathogens. While medications are used to control infections and promote growth, excessive antibiotic use in poultry disrupts this balance, leading to negative health effects. To promote a balanced intestinal microbiota in chickens, beneficial microbes can be provided through synbiotic feed additives. This strategy can improve gut health for better nutrient absorption, strengthen mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue to enhance immunity, and potentially reduce reliance on antibiotics. Synbiotics generally have beneficial effects on host biological functions, acting as immunomodulators and promoting growth in chickens. They help limit pathogen colonization and enhance overall performance. Therefore, poultry producers should be encouraged to incorporate synbiotic-based feed supplements.
Downloads
References
Berihun AM. Effects of Carica Papaya Leaves and Fermented Fish Waste on the Production Performance of Broiler Chickens. Journal of World’s Poultry Science. 2024;3(3):53-61. [DOI]
Shang Y, Kumar S, Oakley B, Kim WK. Chicken gut microbiota: importance and detection technology. Frontiers in veterinary science. 2018;5:254. [PMID: 30406117] [PMCID: PMC6206279] [DOI]
Lou C, Chen Z, Bai Y, Chai T, Guan Y, Wu B. Exploring the microbial community structure in the chicken house environment by metagenomic analysis. Animals. 2023;14(1):55. [PMID: 38200786] [PMCID: PMC10778276] [DOI]
Díaz Carrasco JM, Redondo LM, Casanova NA, Fernandez Miyakawa ME. The role of farm environment and management in shaping the gut microbiota of poultry. Gut microbiota, immunity, and health in production animals: Springer; 2022. p. 193-224. [DOI]
Clavijo V, Morales T, Vives-Flores MJ, Reyes Muñoz A. The gut microbiota of chickens in a commercial farm treated with a Salmonella phage cocktail. Scientific reports. 2022;12(1):991. [PMID: 35046416] [PMCID: PMC8770602] [DOI]
Zhou Q, Lan F, Li X, Yan W, Sun C, Li J, et al. The spatial and temporal characterization of gut microbiota in broilers. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 2021;8:712226. [PMID: 34527716] [PMCID: PMC8435590] [DOI]
Campos PM, Schreier LL, Proszkowiec-Weglarz M, Dridi S. Cecal microbiota composition differs under normal and high ambient temperatures in genetically distinct chicken lines. Scientific Reports. 2023;13(1):16037. [PMID: 37749169] [PMCID: PMC10519933] [DOI]
Szuba-Trznadel A, Rząsa A. Feed additives oF bacterial origin as an immunoprotective or immunostimulating Factor–a review. Annals of Animal Science. 2023;23(4):1009-20. [DOI]
Shehata AA, Yalçın S, Latorre JD, Basiouni S, Attia YA, Abd El-Wahab A, et al. Probiotics, prebiotics, and phytogenic substances for optimizing gut health in poultry. Microorganisms. 2022;10(2):395. [PMID: 35208851] [PMCID: PMC8877156] [DOI]
Li G, Wang X, Liu Y, Gong S, Yang Y, Wang C, et al. Bile acids supplementation modulates lipid metabolism, intestinal function, and cecal microbiota in geese. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2023;14:1185218. [PMID: 37303790] [PMCID: PMC10250614] [DOI]
Velkova L, Dolashki A, Petrova V, Pisareva E, Kaynarov D, Kermedchiev M, et al. Antibacterial properties of peptide and protein fractions from Cornu aspersum mucus. Molecules. 2024;29(12):2886. [PMID: 38930951] [PMCID: PMC11206429] [DOI]
Montoro-Dasi L, Lorenzo-Rebenaque L, Marco-Fuertes A, Vega S, Marin C. Holistic strategies to control Salmonella Infantis: an emerging challenge in the European broiler sector. Microorganisms. 2023;11(7):1765. [PMID: 37512937] [PMCID: PMC10386103] [DOI]
Johnson-Henry KC, Abrahamsson TR, Wu RY, Sherman PM. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis. Advances in nutrition. 2016;7(5):928-37. [PMID: 27633108] [PMCID: PMC5015037] [DOI]
Acharya A, Devkota B, Basnet HB, Barsila SR. Effects of different levels of synbiotic administration on growth performance and response to post-hatch necrotic enteritis in Cobb-500 broilers. Discover Life. 2024;54(1):24. [DOI]
Murphy K, Ross RP, Ryan CA, Dempsey EM, Stanton C. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis. Frontiers in nutrition. 2021;8:667188. [PMID: 34557508] [PMCID: PMC8453148] [DOI]
Waite D. The gut microbiome of the critically endangered kakapo: University of Auckland; 2015.
Chang C, Zhang Q, Wang H, Chu Q, Zhang J, Yan Z, et al. Dietary metabolizable energy and crude protein levels affect pectoral muscle composition and gut microbiota in native growing chickens. Poultry Science. 2023;102(2):102353. [PMID: 36473379] [PMCID: PMC9720343] [DOI]
Volf J, Polansky O, Varmuzova K, Gerzova L, Sekelova Z, Faldynova M, et al. Transient and prolonged response of chicken cecum mucosa to colonization with different gut microbiota. PLoS One. 2016;11(9):e0163932. [PMID: 27685470] [PMCID: PMC5042506] [DOI]
Kumar S, Chen C, Indugu N, Werlang GO, Singh M, Kim WK, et al. Effect of antibiotic withdrawal in feed on chicken gut microbial dynamics, immunity, growth performance and prevalence of foodborne pathogens. PloS one. 2018;13(2):e0192450. [PMID: 29444134] [PMCID: PMC5812630] [DOI]
Nascimento ML, Serrano I, Cunha E, Lopes F, Pascoal P, Pereira M, et al. Exploring the Gastrointestinal Microbiome of Eurasian Griffon Vultures (Gyps fulvus) Under Rehabilitation in Portugal and Their Potential Role as Reservoirs of Human and Animal Pathogens. Veterinary Sciences. 2024;11(12):622. [PMID: 39728962] [PMCID: PMC11680295] [DOI]
Kers JG, Velkers FC, Fischer EA, Hermes GD, Stegeman JA, Smidt H. Host and environmental factors affecting the intestinal microbiota in chickens. Frontiers in microbiology. 2018;9:235. [PMID: 29503637] [PMCID: PMC5820305] [DOI]
Hailu E, Demessie Y, Mulaw A. Effect of vitamin supplementation on egg production, egg quality, and mortality of Sasso chickens. Veterinary Medicine: Research and Reports. 2022:85-90. [PMID: 35509292] [PMCID: PMC9059340] [DOI]
Cammarota G, Ianiro G, Bibbo S, Gasbarrini A. Gut microbiota modulation: probiotics, antibiotics or fecal microbiota transplantation? Internal and emergency medicine. 2014;9(4):365-73. [PMID: 24664520] [DOI]
Horyanto D. Early Colonisation of Bacillus Probiotics in Broilers: CQUniversity; 2024.
Fan Y, Ju T, Bhardwaj T, Korver DR, Willing BP. Week-old chicks with high Bacteroides abundance have increased short-chain fatty acids and reduced markers of gut inflammation. Microbiology Spectrum. 2023;11(2):e03616-22. [PMID: 36719194] [PMCID: PMC10100795] [DOI]
Marcolla CS, Ju T, Willing BP. Cecal Microbiota development and physiological responses of broilers following early life microbial inoculation using different delivery methods and microbial sources. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2023;89(5):e00271-23. [PMID: 37098952] [PMCID: PMC10231219] [DOI]
Yin H-c, Liu Z-d, Zhang W-w, Yang Q-z, Yu T-f, Jiang X-j. Chicken intestinal microbiota modulation of resistance to nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus infection through IFN-I. Microbiome. 2022;10(1):162. [PMID: 36192807] [PMCID: PMC9527382] [DOI]
Ding J, Dai R, Yang L, He C, Xu K, Liu S, et al. Inheritance and establishment of gut microbiota in chickens. Frontiers in microbiology. 2017;8:1967. [PMID: 29067020] [PMCID: PMC5641346] [DOI]
Kayal A, Stanley D, Radovanovic A, Horyanto D, Van TTH, Bajagai YS. Controlled intestinal microbiota colonisation in broilers under the industrial production system. Animals. 2022;12(23):3296. [PMID: 36496817] [PMCID: PMC9740664] [DOI]
Qiu K, Cai H, Wang X, Liu G. Effects of peroral microbiota transplantation on the establishment of intestinal microorganisms in a newly-hatched chick model. Agriculture. 2023;13(5):1001. [DOI]
Villumsen KR, Sandvang D, Vestergård G, Olsen MSR, Juul J, Dencker M, et al. Effects of a novel, non-invasive pre-hatch application of probiotic for broilers on development of cecum microbiota and production performance. Animal microbiome. 2023;5(1):41. [PMID: 37670379] [PMCID: PMC10478294] [DOI]
Zaytsoff SJ, Montina T, Boras VF, Brassard J, Moote PE, Uwiera RR, et al. Microbiota transplantation in day-old broiler chickens ameliorates necrotic enteritis via modulation of the intestinal microbiota and host immune responses. Pathogens. 2022;11(9):972. [PMID: 36145404] [PMCID: PMC9503007] [DOI]
Ding G, Yang X, Li Y, Wang Y, Du Y, Wang M, et al. Gut microbiota regulates gut homeostasis, mucosal immunity and influences immune-related diseases. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2025;480(4):1969-81. [PMID: 39060829] [DOI]
Chen L, Bai X, Wang T, Liu J, Miao X, Zeng B, et al. Gut microbial diversity analysis of different native chickens and screening of chicken-derived probiotics. Animals. 2023;13(23):3672. [PMID: 38067023] [PMCID: PMC10705773] [DOI]
Hamasalim HJ. Synbiotic as feed additives relating to animal health and performance. Advances in Microbiology. 2016;6(04):288. [DOI]
Richards P, Leeming G, Fothergill J, Bernardeau M, Wigley P. Topical Application of Adult Caecal Contents to Eggs Transplants Spore-Forming Microbiota but Not Other Members of the Microbiota to Chicks. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2019;86(5):e02387-19. [PMID: 31862722] [PMCID: PMC7028958] [DOI]
Kocot AM, Jarocka-Cyrta E, Drabińska N. Overview of the importance of biotics in gut barrier integrity. International journal of molecular sciences. 2022;23(5):2896. [PMID: 35270039] [PMCID: PMC8911280] [DOI]
Yadav S, Jha R. Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. Journal of animal science and biotechnology. 2019;10(1):2. [PMID: 30651986] [PMCID: PMC6332572] [DOI]
Waseem H, Jameel S, Ali J, Saleem Ur Rehman H, Tauseef I, Farooq U, et al. Contributions and challenges of high throughput qPCR for determining antimicrobial resistance in the environment: a critical review. Molecules. 2019;24(1):163. [PMID: 30609875] [PMCID: PMC6337382] [DOI]
Śliżewska K, Markowiak-Kopeć P, Żbikowski A, Szeleszczuk P. The effect of synbiotic preparations on the intestinal microbiota and her metabolism in broiler chickens. Scientific reports. 2020;10(1):4281. [PMID: 32152423] [PMCID: PMC7062770] [DOI]
Rahman MN, Ahmed M, Mollah BR, Faiyaz I, Foysal A. Effect of Synbiotic, Probiotic and Neem Leaf as Alternatives to Antibiotic in Broiler Chicken Diets. 2022. [DOI]
Prentza Z, Castellone F, Legnardi M, Antlinger B, Segura-Wang M, Kefalas G, et al. Administration of a multi-genus synbiotic to broilers: Effects on gut health, microbial composition and performance. Animals. 2022;13(1):113. [PMID: 36611722] [PMCID: PMC9817898] [DOI]
Khan S, Chand N, Hafeez A, Ahmad N. Efficacy of Gum Arabic and Bacillus subtilis Alone and in Synbiotic Form on Overall Performance, Visceral and Lymphoid Organs Along with Intestinal Histomorphology and Selected Pathogenic Bacteria in Broiler Chickens. Pakistan Journal of Zoology. 2024;56(2). [DOI]
Al Amaz S, Mishra B. Embryonic thermal manipulation: a potential strategy to mitigate heat stress in broiler chickens for sustainable poultry production. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology. 2024;15(1):75. [PMID: 38831417] [PMCID: PMC11149204] [DOI]
Lorenzo-Rebenaque L, Casto-Rebollo C, Diretto G, Frusciante S, Rodríguez JC, Ventero M-P, et al. Modulation of caecal microbiota and metabolome profile in salmonella-infected broilers by phage therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023;24(20):15201. [PMID: 37894882] [PMCID: PMC10607084] [DOI]
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T, Gindulyte A, He J, He S, et al. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic acids research. 2023;51(D1):D1373-D80. [PMID: 36305812] [PMCID: PMC9825602] [DOI]
Akoy RAM. The effects of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics on gut flora, immune function and blood characteristics of broilers. 2015.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Asnakew Mulaw Berihun (Corresponding Author); Zenebe Jemere, Bemrew Admassu, Dejen Takele, Yitayew Demessie (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.