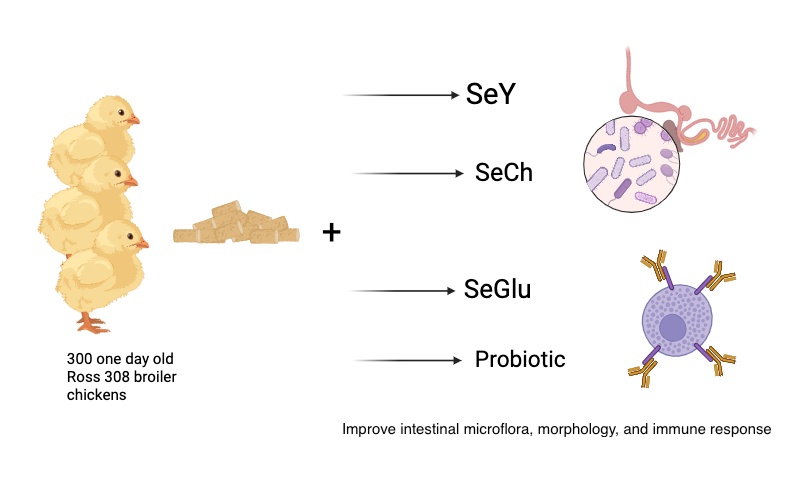
Intestinal Microflora, Morphology, and Immune Response in Broiler Chickens Fed Various Organic Selenium and Probiotic Sources
Keywords:
Broiler, Intestine, Selenium-chitosan, Selenized glucose, ProbioticAbstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of selenium-enriched yeast (SeY), selenium-chitosan (SeCh), and selenized glucose (SeGlu) as organic selenium sources, probiotics, and the interactions between selenium sources and probiotics on the intestinal microflora, intestinal morphology, and immune response in broilers. In a 3×2 factorial treatment design, 300 one-day-old Ross 308 broiler chickens were randomly assigned to six experimental groups. Selenium sources (0.3 mg/kg SeY, SeCh, and SeGlu) and probiotic levels (0 and 100 mg/kg) were among the factors investigated. Five-floor pens with 10 birds each have been used to replicate the treatments. Compared to SeY, broiler chickens fed SeCh or SeGlu had lower coliform bacteria counts, higher lactic acid bacteria counts, and lactic acid bacteria/coliform ratios in the ileum (p<0.05). Interaction results showed that birds fed diets supplemented with SeCh and SeGlu plus probiotics had higher villus height per crypt depth, villus surface area, and goblet cell density, as well as lower epithelial cell layer thickness in the ileum (p<0.05). At 28 and 42 days, birds fed diets supplemented with SeCh and SeGlu had the highest total antibody response to sheep red blood cells, IgG, and IgM titers (p<0.05). Birds fed diets supplemented with SeCh and SeGlu plus Probiotic had higher IgG levels than SeY without Probiotic (p<0.05). As a result, it is possible to conclude that SeCh and SeGlu, as novel and simple Se sources plus Probiotic, can improve intestinal microflora, morphology, and immune response in broiler chickens when compared to SeY alone.
Downloads
References
Zhou X, Wang Y. Influence of dietary nano elemental selenium on growth performance, tissue selenium distribution, meat quality, and glutathione peroxidase activity in Guangxi Yellow chicken. Poultry Science. 2011;90(3):680-6.[PMID: 21325242] [DOI]
Li J, Shen B, Nie S, Duan Z, Chen K. A combination of selenium and polysaccharides: Promising therapeutic potential. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2019;206:163-73.[PMID: 30553309] [DOI]
Xia IF, Cheung JS, Wu M, Wong KS, Kong HK, Zheng XT. Dietary chitosan-selenium nanoparticles (CTS-SeNPs) enhance immunity and disease resistance in zebrafish. Fish & Shellfish Immunology. 2019;87:449-59.[PMID: 30703551] [DOI]
Mahmoud HED, Ijiri D, Ebeid TA, Ohtsuka A. Effects of dietary nano-selenium supplementation on growth performance, antioxidative status, and immunity in broiler chickens under thermoneutral and high ambient temperature conditions. Journal of Poultry Science. 2016;53(4):274-83.[PMID: 32908394] [PMCID: PMC7477162] [DOI]
Silva VA, Clemente AHS, Nogueira BRF, De Carvalho AC, De Freitas LFVB, Ramos ADLS. Supplementation of selenomethionine at different ages and levels on meat quality, tissue deposition, and selenium retention in broiler chickens. Poultry Science. 2019;98(5):2150-9.[PMID: 30590669] [DOI]
Bakhshalinejad R, Akbari Moghaddam Kakhki R, Zoidis E. Effects of different dietary sources and levels of selenium supplements on growth performance, antioxidant status and immune parameters in Ross 308 broiler chickens. British Poultry Science. 2018;59(1):81-91.[PMID: 28906132] [DOI]
Dalia AM, Loh TC, Sazili AQ, Jahromi MF, Samsudin AA. Effects of vitamin E, inorganic selenium, bacterial organic selenium, and their combinations on immunity response in broiler chickens. BMC Veterinary Research. 2018;14:1-10.[PMID: 30143038] [PMCID: PMC6109295] [DOI]
Dalia AM, Loh TC, Sazili AQ, Samsudin AA. Influence of bacterial organic selenium on blood parameters, immune response, selenium retention and intestinal morphology of broiler chickens. BMC Veterinary Research. 2020;16:1-10.[PMID: 32993790] [PMCID: PMC7526326] [DOI]
Ahmadi M, Ahmadian A, Seidavi AR. Effect of different levels of nano-selenium on performance, blood parameters, immunity, and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens. Poultry Science Journal. 2018;6:99-108[DOI]
Bakhshalinejad R, Hassanabadi A, Swick RA. Dietary sources and levels of selenium supplements affect growth performance, carcass yield, meat quality, and tissue selenium deposition in broilers. Animal Nutrition. 2019;5(3):256-63.[PMID: 31528727] [PMCID: PMC6737497] [DOI]
Khajeh Bami M, Afsharmanesh M, Salarmoini M, Ebrahimnejad H. Effects of selenium-chitosan on intestinal microflora, intestinal histomorphology, and immune response of broiler chickens. Livestock Science. 2022;255:104806[DOI]
Marković R, Ćirić J, Starčević M, Šefer D, Baltić MŽ. Effects of selenium source and level in diet on glutathione peroxidase activity, tissue selenium distribution, and growth performance in poultry. Animal Health Research Reviews. 2018;19(2):166-76.[PMID: 30683170] [DOI]
Lu J, Qu L, Shen MM, Wang XG, Guo J, Hu YP, et al. Effects of high-dose selenium-enriched yeast on laying performance, egg quality, clinical blood parameters, organ development, and selenium deposition in laying hens. Poultry Science. 2019;98(6):2522-30.[PMID: 30715535] [DOI]
Zhao M, Sun Q, Khogali MK, Liu L, Geng T, Yu L. Dietary selenized glucose increases selenium concentration and antioxidant capacity of the liver, oviduct, and spleen in laying hens. Biological Trace Element Research. 2021;199:4746-52.[PMID: 33506411] [DOI]
Victor H, Zhao B, Mu Y, Dai X, Wen Z, Gao Y. Effects of Se-chitosan on the growth performance and intestinal health of the loach Paramisgurnus dabryanus (Sauvage). Aquaculture. 2019;498:263-70[DOI]
Wang L, Xiao JX, Hua Y, Xiang XW, Zhou YF, Ye L. Effects of dietary selenium polysaccharide on growth performance, oxidative stress, and tissue selenium accumulation of juvenile black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Aquaculture. 2019;503:389-95[DOI]
Huang S, Yang W, Huang G. Preparation and activities of selenium polysaccharide from plant such as Grifola frondosa. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2020;242:116409.[PMID: 32564830] [DOI]
Zhou W, Li P, Liu J, Yu L. Kilogram-scale production of selenized glucose. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 2020;59(23):10763-7[DOI]
Yuan D, Zhan XA, Wang YX. Effect of selenium sources on the expression of cellular glutathione peroxidase and cytoplasmic thioredoxin reductase in the liver and kidney of broiler breeders and their offspring. Poultry Science. 2012;91(4):936-42.[PMID: 22399733] [DOI]
Aviagen. Nutrition Specifications Manual: Ross 308. Scotland, UK: Aviagen Ltd.; 2014.
Khajeh Bami M, Afsharmanesh M, Espahbodi M, Esmaeilzadeh E. Effects of dietary nano-selenium supplementation on broiler chicken performance, meat selenium content, intestinal microflora, intestinal morphology, and immune response. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology. 2022;69:126897.[PMID: 34814061] [DOI]
Wegmann TG, Smithies O. A simple hemagglutination system requiring small amounts of red cells and antibodies. Transfusion. 1966;6(1):67-73[DOI]
Zhai Q, Cen S, Li P, Tian F, Zhao J, Zhang H. Effects of dietary selenium supplementation on intestinal barrier and immune responses associated with its modulation of gut microbiota. Environmental Science & Technology Letters. 2018;5(12):724-30[DOI]
Kasaikina MV, Kravtsova MA, Lee BC, Seravalli J, Peterson DA, Walter J, et al. Dietary selenium affects host selenoproteome expression by influencing the gut microbiota. The FASEB Journal. 2011;25(7):2492-9.[PMID: 21493887] [PMCID: PMC3114522] [DOI]
Guo FC, Williams BA, Kwakkel RP, Li HS, Li XP, Luo JY. Effects of mushroom and herb polysaccharides, as alternatives for an antibiotic, on the cecal microbial ecosystem in broiler chickens. Poultry Science. 2004;83(2):175-82.[PMID: 14979567] [DOI]
Khan SH, Ansari J, Haq AU, Abbas G. Black cumin seeds as phytogenic product in broiler diets and its effects on performance, blood constituents, immunity and caecal microbial population. Italian Journal of Animal Science. 2012;11(4):e77[DOI]
Muhammad AI, Mohamed DA, Chwen LT, Akit H, Samsudin AA. Effect of selenium sources on laying performance, egg quality characteristics, intestinal morphology, microbial population and digesta volatile fatty acids in laying hens. Animals. 2021;11(6):1681.[PMID: 34199988] [PMCID: PMC8228612] [DOI]
Lv CH, Wang T, Regmi N, Chen X, Huang K, Liao SF. Effects of dietary supplementation of selenium‐enriched probiotics on production performance and intestinal microbiota of weanling piglets raised under high ambient temperature. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition. 2015;99(6):1161-71.[PMID: 25900236] [DOI]
Gangadoo S, Bauer BW, Bajagai YS, Van TTH, Moore RJ, Stanley D. In vitro growth of gut microbiota with selenium nanoparticles. Animal Nutrition. 2019;5(4):424-31.[PMID: 31890921] [PMCID: PMC6920403] [DOI]
Tang D, Li Z, Mahmood T, Liu D, Hu Y, Guo Y. The association between microbial community and ileal gene expression on intestinal wall thickness alterations in chickens. Poultry Science. 2020;99(4):1847-61.[PMID: 32241465] [PMCID: PMC7587722] [DOI]
Choct M. Managing gut health through nutrition. British Poultry Science. 2009;50(1):9-15.[PMID: 19234925] [DOI]
Boostani A, Sadeghi AA, Mousavi SN, Chamani M, Kashan N. Effects of organic, inorganic, and nano-Se on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, cellular and humoral immune responses in broiler chickens exposed to oxidative stress. Livestock Science. 2015;178:330-6[DOI]
Mohammadi E, Janmohammadi H, Olyayee M, Helan JA, Kalanaky S. Nano selenium improves humoral immunity, growth performance and breast-muscle selenium concentration of broiler chickens. Animal Production Science. 2020;60(16):1902-10[DOI]
Rao SVR, Prakash B, Raju MVLN, Panda AK, Poonam S, Murthy OK. Effect of supplementing organic selenium on performance, carcass traits, oxidative parameters and immune responses in commercial broiler chickens. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Science. 2013;26(2):247-.[PMID: 25049783] [PMCID: PMC4093145] [DOI]
Cai SJ, Wu CX, Gong LM, Song T, Wu H, Zhang LY. Effects of nano-selenium on performance, meat quality, immune function, oxidation resistance, and tissue selenium content in broilers. Poultry Science. 2012;91(10):2532-9.[PMID: 22991539] [DOI]
Moghaddam AZ, Hamzekolaei MM, Khajali F, Hassanpour H. Role of selenium from different sources in prevention of pulmonary arterial hypertension syndrome in broiler chickens. Biological Trace Element Research. 2017;180:164-70.[PMID: 28317078] [DOI]
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Asma Shokrinejad Gerdin (Author); Mohsen Afsharmanesh, Mohammad Khajeh Bami (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.