NPY1 and MC3/MC4 receptors mediate BDNF-induced hypophagia in 5-day-old chickens
Keywords:
Appetite, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, Melanocortin, Neuropeptide Y, ChickensAbstract
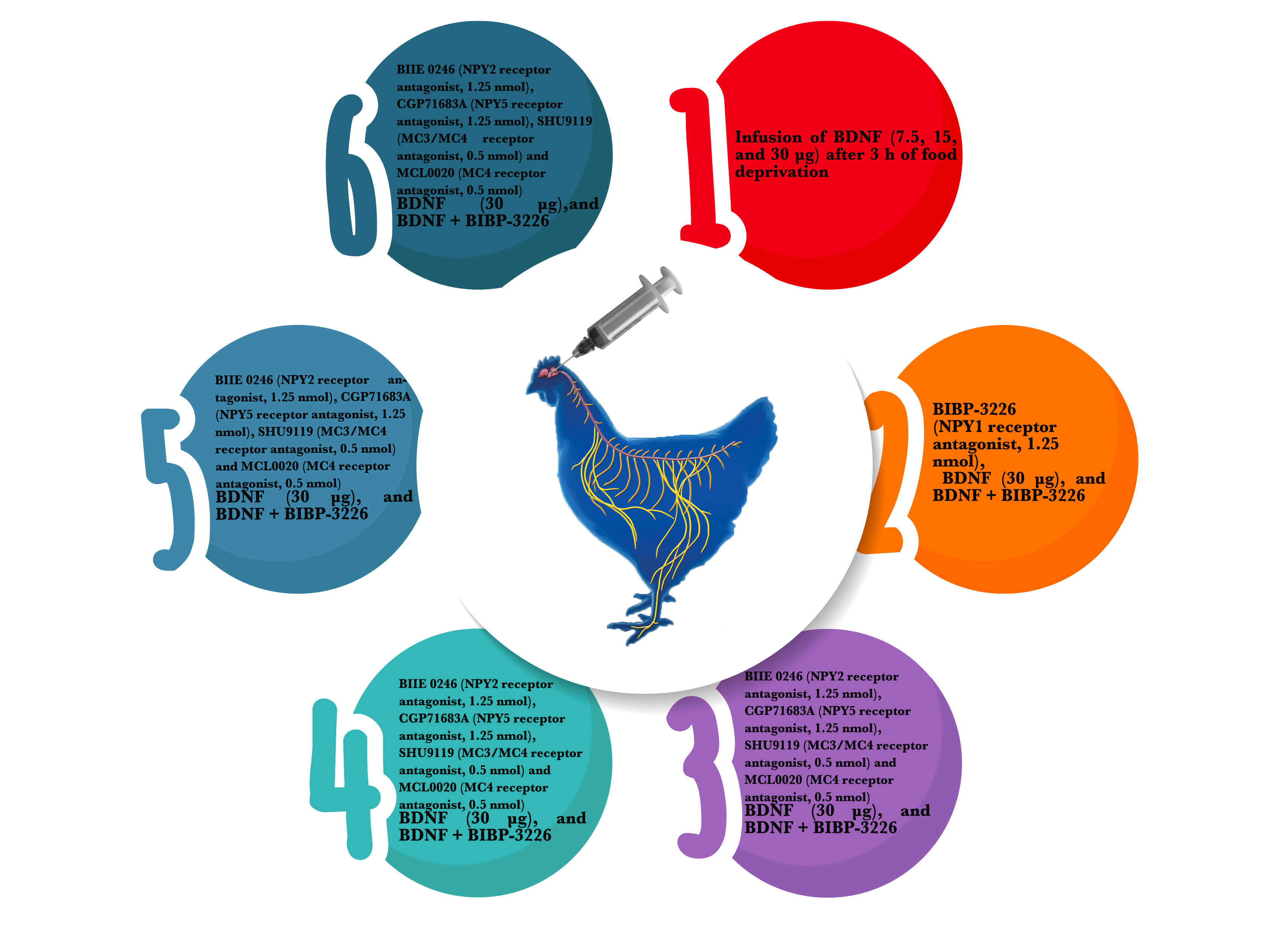
Distinguishing the variables that control craving and examining the interaction between them can improve the efficiency of livestock breeding, genetic modification, and drug treatments of obesity-related complications. Hence, in the current study, we investigated the interaction between neuropeptide Y and melanocortinergic systems with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in regulating broilers' feed intake. The present study was conducted on 264 broiler chickens in 6 experiments. In experiment 1, chickens received intracerebroventricular (ICV) infusion of BDNF (7.5, 15, and 30 μg) after 3 h of food deprivation. BIBP-3226 (NPY1 receptor antagonist, 1.25 nmol), BDNF (30 μg), and BDNF + BIBP-3226 were administrated in the second treatment. Experiments 3-6 were similar to treatment 2, except birds were infused with BIIE 0246 (NPY2 receptor antagonist, 1.25 nmol), CGP71683A (NPY5 receptor antagonist, 1.25 nmol), SHU9119 (MC3/MC4 receptor antagonist, 0.5 nmol) and MCL0020 (MC4 receptor antagonist, 0.5 nmol) instead of BIBP-3226. Then, cumulative meal intake was recorded for 2 hours. Based on observations, BDNF injection (15 and 30 μg) caused significant hypophagia at all test times (p<0.05). The co-infusion of NPY2 and NPY5 receptor antagonists with BDNF did not affect BDNF-induced hypophagia (p>0.05), while the infusion of NPY1 receptor antagonist + BDNF caused a significant strengthening of this effect (p<0.05). Also, despite the lack of significant effect of MC4 receptor antagonist + BDNF administration on the appetite-reducing effect of BDNF (p>0.05), simultaneous infusion of MC3/MC4 receptor antagonist and BDNF suppressed hypophagia (p<0.05). Finally, it appears that MC3/MC4 and NPY1 receptors mediate BDNF-induced hypophagia in 5-day-old broiler chickens.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Hamed Zarei, Ghazale Kiaee, Morteza Zendehdel (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.