Evaluation of Serological Response of Low and Highly Pathogenic Influenza Vaccines in Japanese Quails
Abstract
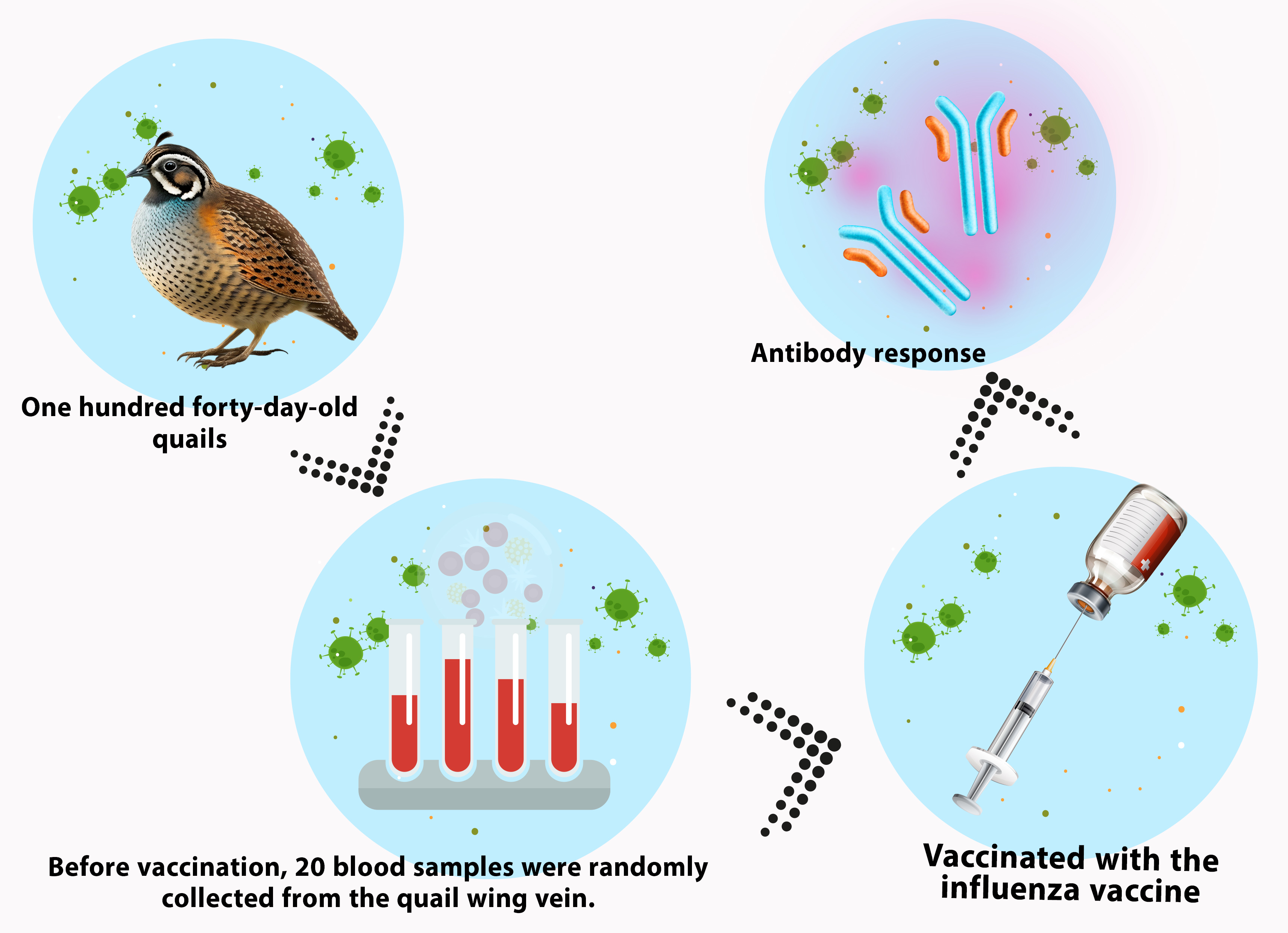
Avian influenza A virus (AIV) causes one of the most transmissible diseases. This virus can infect the quails and be spread to other animal species. Vaccination in chickens and ducks has shown that highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses (HPAI) can be controlled. This study evaluated the serological response of low and highly pathogenic influenza vaccines in quails. One hundred forty-day-old quails were divided into seven groups. Before vaccination, 20 blood samples were randomly collected from the quail wing vein. At 21 days of age, Group 2 was vaccinated with the H9N2 vaccine. Quails in Group 4 were vaccinated with the H5N1 influenza vaccine (Harbin). Quails in Group 6 received the H5N1 vaccine (Livaning). At 42 days of age, Groups 3, 5, and 7 were re-vaccinated with the same vaccines as in the previous stage. Blood samples were collected from each group from 20 quails at 20, 42, and 56 days to determine AIV antibodies by the HI test. Three weeks after the second vaccination (H9N2), the antibody titer was higher than in the group that received the vaccine once, but the difference was insignificant. The antibody titer after the second Harbin vaccine (H5N1) was higher than in the group receiving only one dose, but the difference was negligible. The antibody titer at 63 days was higher in the group that received one dose of the Livaning (H5N1) vaccine, and this difference was significant. After the second vaccination, there was a significant difference in the titers between the two doses of H9N2 and H5N1 for the Livaning and Harbin vaccines. The average increase in antibody production following the two doses of H9N2 and Harbin vaccines showed similar trends. However, the Livaning vaccine produced a significantly higher antibody response than the other two (p<0.05).
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Elahah Golgol (Author); Mansour Mayahi (Corresponding Author); Zahra Boroomand, Ali Zaherzade (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.