Comparison of isolation and histopathology methods in diagnosis of pigeon tuberculosis
Abstract
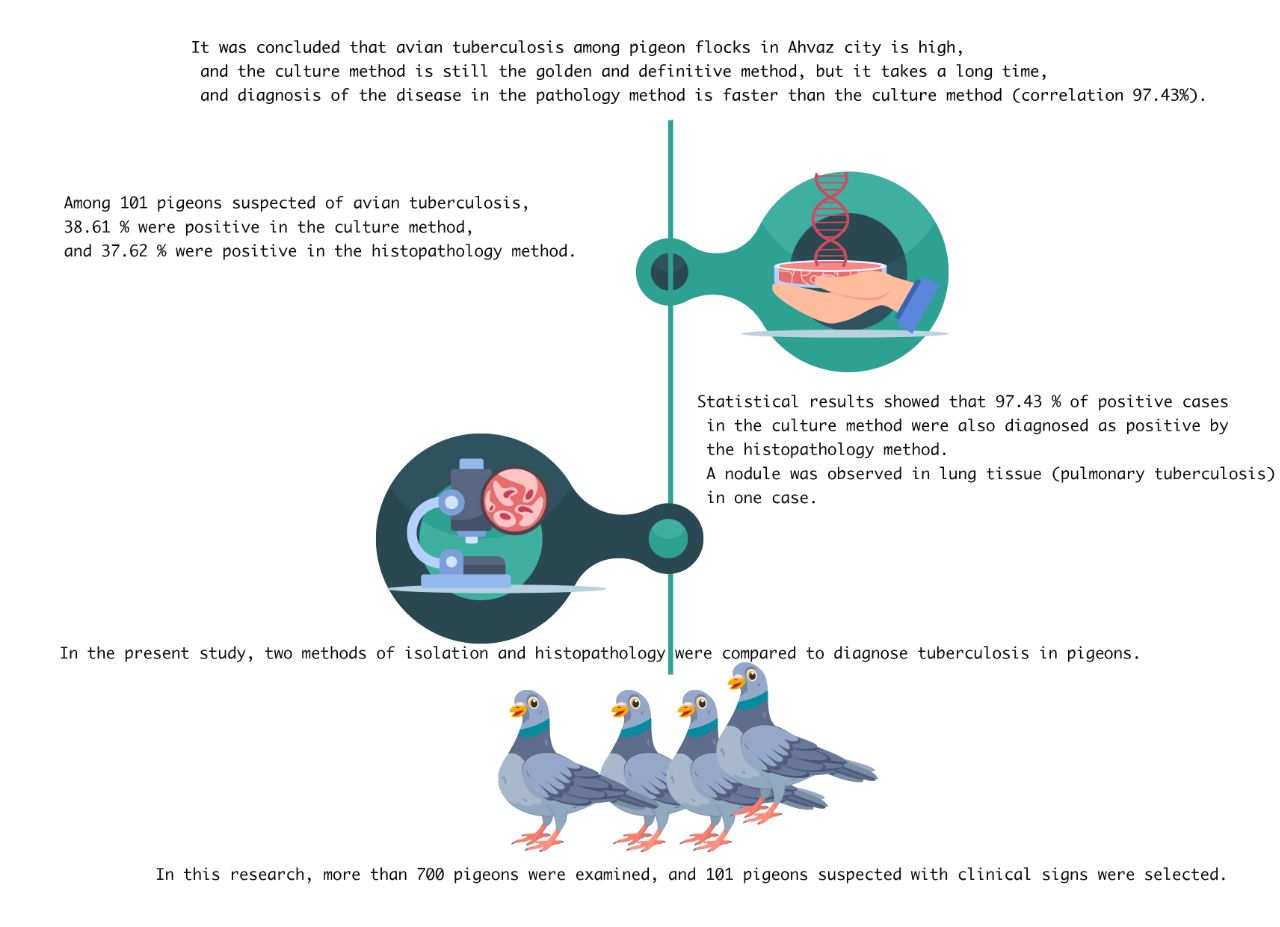
Avian tuberculosis is one of the most important diseases that affect most types of birds, such as laying hens, pigeons, turkeys, parrots, pheasants, waterfowl, and wild birds. Tuberculosis is the most important infectious disease between humans and animals. Avian tuberculosis often affects the gastrointestinal tract of birds. Several species of mycobacteria can contribute to avian tuberculosis, but the disease is most commonly caused by Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium genavense. Culture methods are used to diagnose mycobacterial infection in birds defnitively. In the present study, two methods of isolation diagnosis and pathology were compared to the diagnosis of tuberculosis in pigeons. In this study, among 101 pigeons suspected to avian tuberculosis, 38.61 % were found positive in the culture method and 37.62 % were found positive in the histopathology method. Statistical results showed, that 97.43 % of positive cases in culture method were also diagnosed as positive by the histopathology method. In one case of tuberculosis a nodule was observed in lung tissue (pulmonary tuberculosis). It was concluded that avian tuberculosis among pigeon flocks in Ahvaz city is high and culture method still the golden and definitive method but need prolonged time, but pathology method is faster than culture method with high correlation (97.43%) with culture method.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mahsa Lari Baghal, Mansour Mayahi, Nader Mosavari, Zahra Boroomand, Mohammad Islampanah (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.