Study of resistance to cephalosporin compounds in Salmonella spp. and Salmonella Typhimurium isolated from turkeys
Abstract
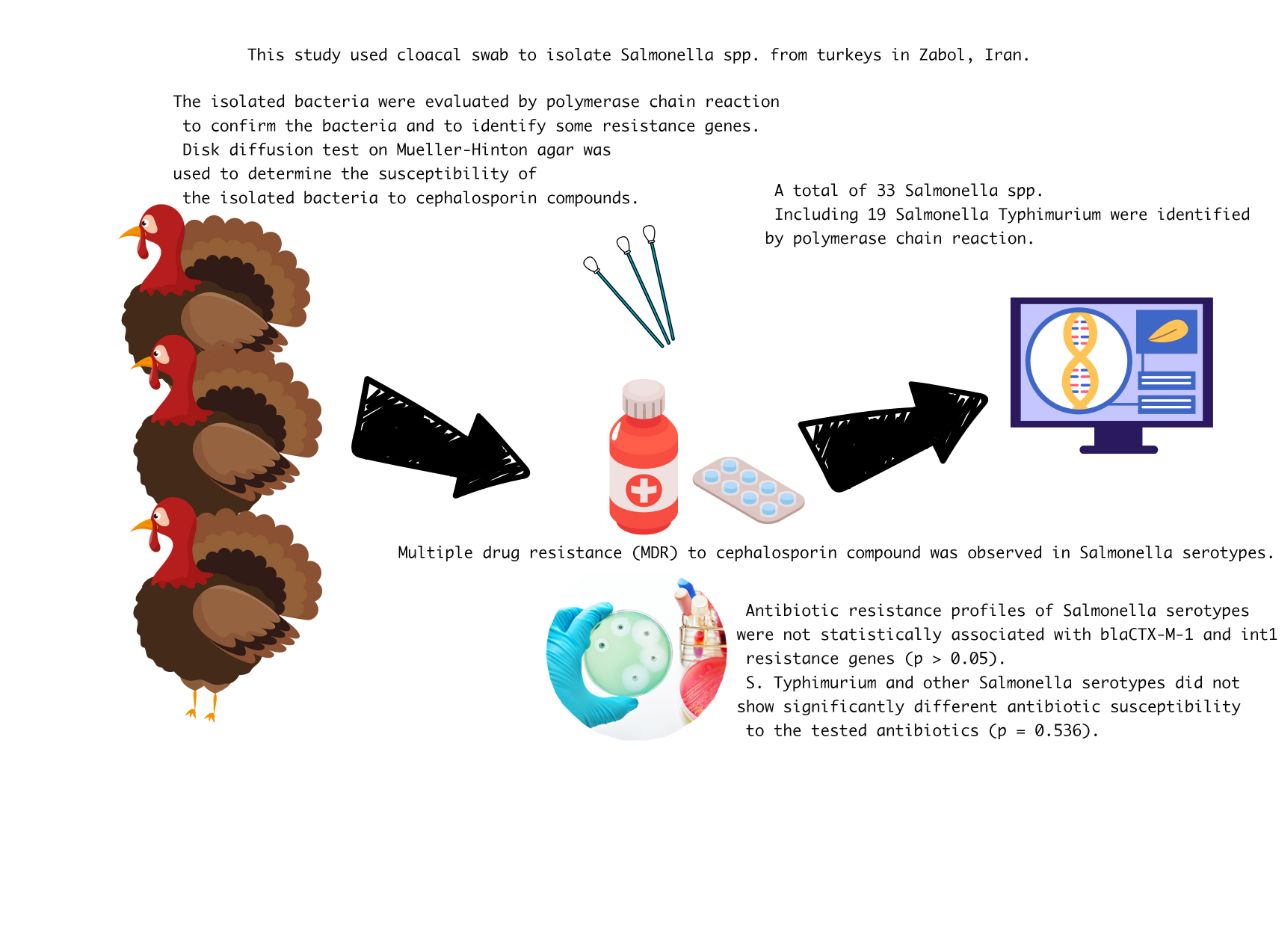
The high consumption of antimicrobial agents in livestock is a global problem that can increase the antibiotic resistance of human and animal bacteria such as Salmonella serotypes. In this study, cloacal swab was used to isolate Salmonella spp. from turkeys in Zabol, Iran. The isolated bacteria were evaluated by polymerase chain reaction to confirm the bacteria and to identify some resistance genes. Disk diffusion test on Mueller-Hinton agar was used to determine the susceptibility of the isolated bacteria to cephalosporin compounds. A total of 33 Salmonella spp. including 19 Salmonella Typhimurium were identified by polymerase chain reaction. Multiple drug resistance (MDR) to cephalosporin compound was observed in Salmonella serotypes. Antibiotics resistance profiles of Salmonella serotypes were not statistically associated with blaCTX-M-1 and int1 resistance genes (p > 0.05). S. Typhimurium and other Salmonella serotypes did not show significantly different antibiotic susceptibility to the tested antibiotics (p = 0.536). According to the results, there is a high prevalence of resistance to cephalosporin compounds among Salmonella spp. and S. Typhimurium in Zabol, Iran.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Keyvan Samadi, Mohammad Jahantigh, Reza Esmaeelzadeh Dizaji, Dariush Saadati (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.