Heritability of fertility, hatchability and their relationship with egg quality traits in Japanese quail
Abstract
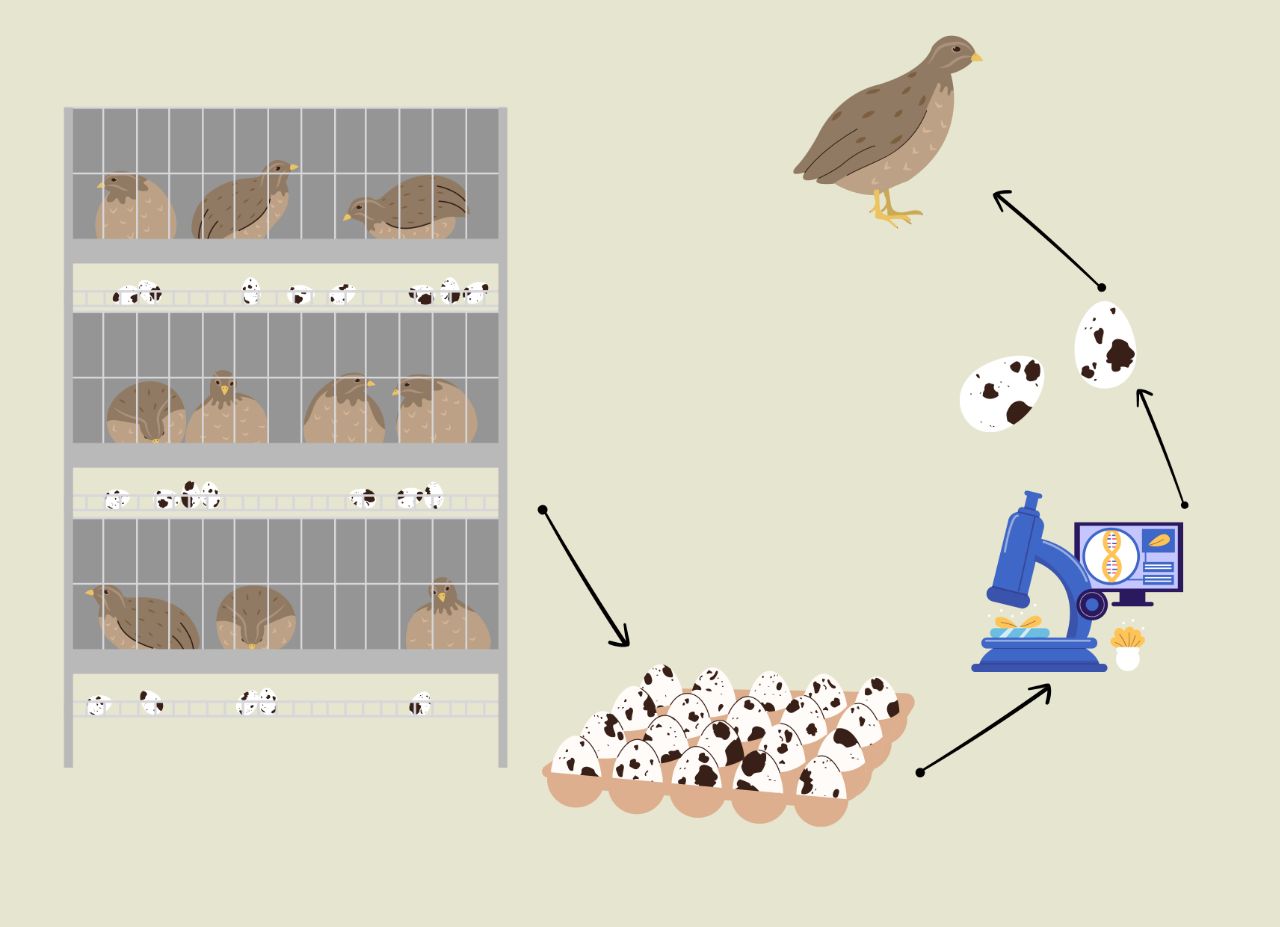
The heritability of fertility, hatchability, and their relationship with egg quality traits was studied in fully pedigreed records of a Japanese quail population. A restricted maximum likelihood (REML) procedure was applied in univariate and bivariate analyses. According to the heritability values of FERT, HFE, and HTE in this population of Japanese quail, the role of genes is low, and it is feasible to improve these traits through environmental conditions effectively. Percentage of fertility (FERT) showed positive genetic correlations with AH, YH, YW, and YI (from 0.18 to 0.65) and negative genetic correlations with AW (-0.21). The high genetic correlations were obtained between HFE and ESI (0.62), between HFE and EST (0.56), between HTE and ESI (0.53), and between HTE and EST (0.51). In conclusion, reproductive traits (fertility and hatchability) can improve through selection for high egg quality traits such as EST, ESI, YH, YW, and YI in Japanese quail.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Batoul Asghari Esfeden, Ali Reza Khanahmadi, Elias Lotfi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.