Different light programs affect the titer of vaccination of Newcastle in broiler chicken
Keywords:
Broiler, Photoperiod, Newcastle disease, Lighting program.Abstract
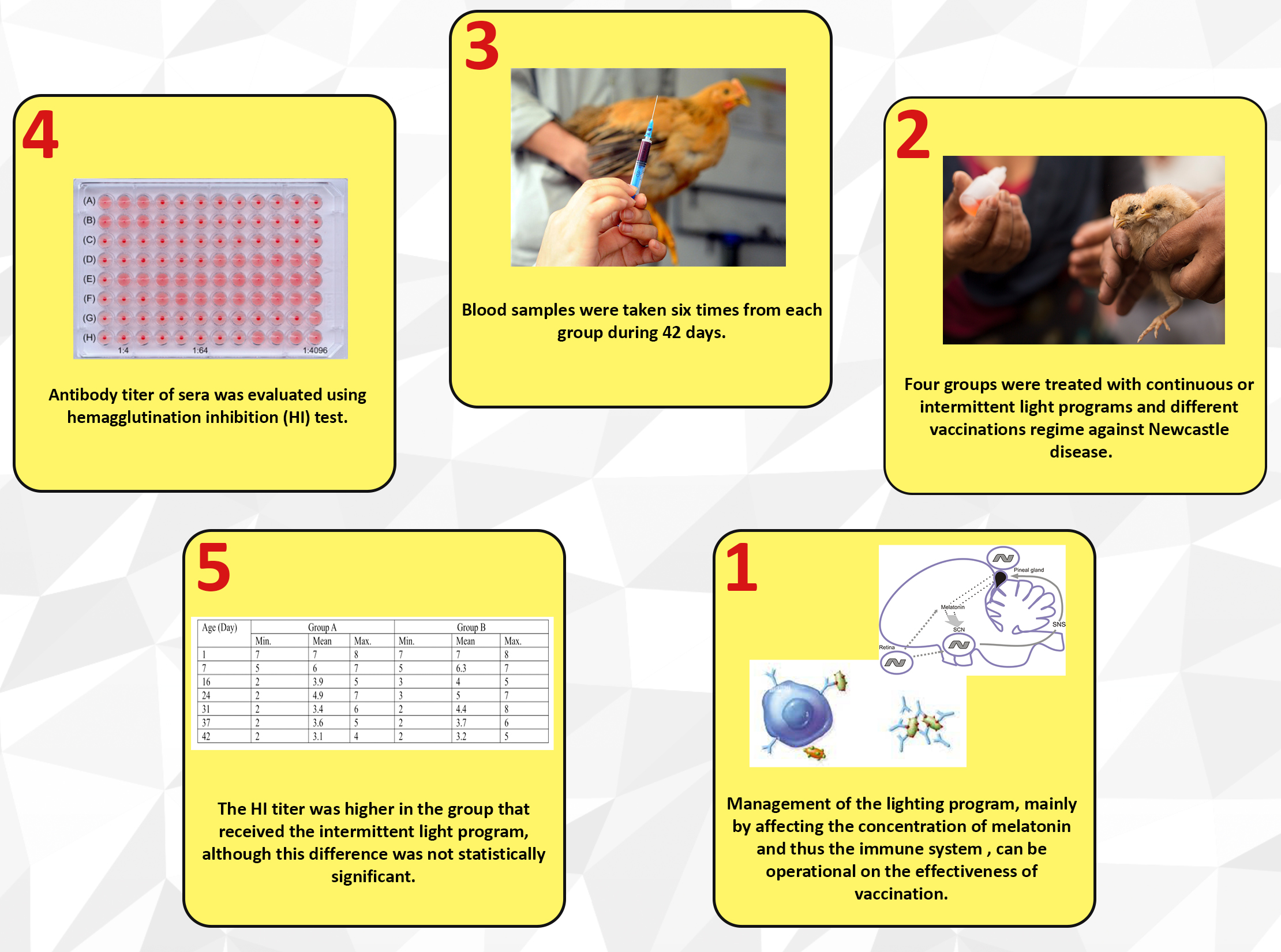
Light is an important factor in the functioning of the body of birds, especially the immune system. Management of the lighting program in closed systems of poultry production, mainly by affecting the concentration of melatonin, can be operational on the effectiveness of vaccination. Newcastle disease can cause extensive damage to the poultry industry. Therefore, its timely diagnosis and assessment of the success of vaccination with methods such as the hemagglutination inhibition test are of particular importance. This study investigated the effect of two photoperiods on antibody titer against Newcastle virus following vaccination. Four groups of Ross broilers were examined for six weeks. Groups A and B received the live Newcastle vaccine twice, and groups C and D were not vaccinated against Newcastle. Groups A and C received a lighting program from the management handbook of Ross Broiler, and groups B and D received the continuous lighting program (23L:1D). During the breeding period, blood samples were taken six times from each group, and the HI test measured the antibody titer. The results showed that despite the higher antibody titer in group B compared to group A, this difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). The feed conversion rate was higher in the groups that received the continuous photoperiod, and their mortality rate was lower than that of the other two groups. Comparing the results of the present study with those of various studies and articles shows the importance of the lighting regime in the success of vaccination.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.